Many workshops and small fabrication facilities operate with single-phase power, while most industrial welding machines are built for three-phase electrical systems. This mismatch often raises a practical question: Can a three-phase welder be converted to run on single-phase power?
While the process sounds simple, it involves more than just rewiring. Converting or adapting a welder’s input power requires a clear understanding of electrical design, load balance, and safety compliance. Below is a comprehensive guide on what’s possible, what to avoid, and the safest ways to achieve reliable welding performance on single-phase power.
I. What is 3-phase and single-phase power?
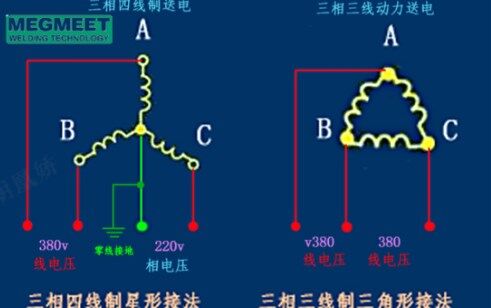
3-Phase Power: Used primarily in industrial facilities, three-phase power delivers electricity through three alternating currents, each offset by 120°. This configuration provides a continuous and balanced flow of power, supporting high-efficiency operation and stable arc performance in heavy-duty welders.
Single-Phase Power: Common in homes and smaller workshops, single-phase power uses one alternating current. While sufficient for light to medium applications, it provides less consistent output and may limit the performance of large industrial welders.
Because of these fundamental electrical differences, a 3-phase welder cannot simply be rewired to operate on single-phase input without proper equipment or design adjustments.
II. Steps to Convert a 3-Phase Welder to a Single-Phase
Step 1: Assess the Welder’s Specifications
Before any modification, review the welder’s nameplate or technical manual to confirm its input voltage, current requirements, and phase configuration.
Some modern inverter welders are multi-voltage or dual-phase compatible (for example, 230/400 V, 1 ph/3 ph). If this is the case, conversion may only involve adjusting internal jumpers or selecting the appropriate input mode.
If your welder is labeled “3-phase only”, direct conversion is not recommended without a power conversion device.
Step 2: Obtain a Phase Converter or Rewiring Kit
If your power supply is single-phase and your welder supports only three-phase input, the most practical solution is to use a phase converter.
Rotary Phase Converter: This device generates a true three-phase output from a single-phase source using an idler motor. It provides balanced power and stable current, making it suitable for industrial-grade welders.
Static Phase Converter: A static converter is smaller and less expensive but can only simulate three-phase power. It may work for smaller welders but usually delivers reduced output capacity.
Digital or VFD-Based Converters: These modern systems can create a balanced three-phase waveform electronically, providing a cleaner and more efficient solution for inverter welders.
Step 3: Rewiring or Installing the Converter
If you are not experienced with electrical systems, it is best to consult a qualified electrician or service engineer to ensure correct installation, grounding, and breaker sizing.
Step 4: Testing and Calibration
After the conversion or installation:
Note that arc characteristics may differ slightly under single-phase input due to current ripple and power factor variations.
Step 5: Observe Safety and Compliance
Always prioritize electrical safety:
Ensure proper grounding and insulation.
Verify that all cables, connectors, and circuit breakers are rated for the welder’s full current draw.
Follow local electrical regulations and safety codes during modification or installation.
Never connect a 3-phase welder directly to single-phase power without a converter — doing so can damage the welder’s internal components or cause serious electrical hazards.
III. Key Considerations Before Conversion
Warranty Implications: Modifying a welder’s input circuit may void its manufacturer warranty. Always check the documentation or consult the manufacturer before proceeding.
Performance Limitations: Even with a converter, single-phase operation may result in reduced output power or lower duty cycle, especially on heavy-duty welding jobs.
Professional Assistance: For complex or high-value equipment, seek assistance from an authorized Megmeet service technician to ensure reliability and safety.
IV. Better Alternative: Single-Phase Inverter Welders
Instead of modifying a three-phase welder, a more practical and reliable solution is to use a modern single-phase inverter-based welding machine.
Today’s inverter welders are engineered with advanced power electronics that allow them to deliver high output efficiency and stable arc performance while operating on standard single-phase 220–240 V power supplies. They use IGBT or MOSFET inverter technology to convert and control current precisely, resulting in smooth arc starts, minimal spatter, and consistent penetration.
Compared with older transformer-based models, single-phase inverter welders offer several key advantages:
High energy efficiency: Reduced power loss and better conversion rates lower electricity consumption.
Stable arc performance: Precise waveform control improves weld quality and reduces rework.
Compact and lightweight design: Easier to transport and install in small workshops or on-site environments.
Wide process compatibility: Suitable for multiple welding methods, including MIG, TIG, and Stick.
Smart control features: Digital displays, pulse settings, and automatic parameter adjustments enhance usability and accuracy.
For most users, especially those operating in single-phase environments, investing in a dedicated single-phase inverter welder is far safer and more cost-effective than retrofitting a three-phase unit. It ensures optimal performance, simplifies setup, and eliminates the risks associated with electrical conversion.
Conclusion
Converting a 3-phase welder to single-phase power isn’t a simple wiring change — it requires careful analysis, proper equipment, and strict adherence to electrical safety standards.
While phase converters can provide a workable solution, the most efficient path is to use a single-phase inverter welder specifically designed for the available power supply.
By understanding the differences between 3-phase and single-phase systems and selecting the right equipment, welders can maintain stable performance, safety, and long-term reliability in any working environment.
Related articles:
1. How Much Power is Consumed by a 3 Phase Welding Machine?
2. Three-phase Welding Machine VS. Single-phase Inverter Welding Machine
3. What is an Inverter Welder & How it Works (Top 6 Inverter Welders)
4. Inverter Welder Problems and How to Solve Them?
5. Inverter vs Transformer Welders: Which One Reigns Supreme in Welding?




