Welding technology has undergone significant advancements over the years, allowing for more precise and efficient fabrication processes. One such innovation is high-frequency Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding (View The Most Complete TIG Welding Basics), which has gained prominence in various industries due to its superior performance and versatile applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of high-frequency TIG welding, exploring its working principles, benefits, and diverse applications across multiple sectors.
I. What is High-Frequency TIG Welding?
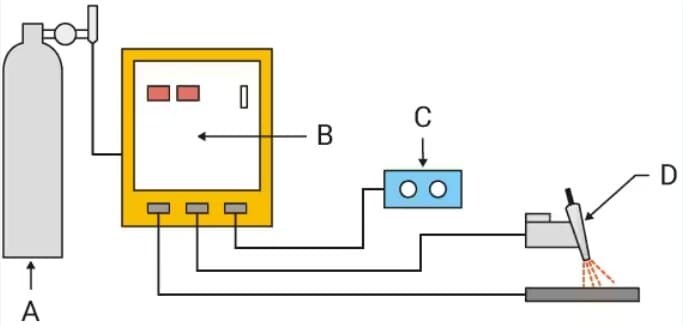
High-frequency TIG welding is an advanced arc welding technique that employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The process involves generating an electric arc between the tungsten electrode and the workpiece, typically metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, copper alloys, and other non-ferrous materials. Unlike traditional TIG welding, high-frequency TIG welding utilizes an external high-frequency power source to initiate and maintain the arc, resulting in improved weld quality and precision.
II. Key Components and Working Principles
High-frequency TIG welding systems consist of several crucial components that facilitate the welding process. These components include the power source, torch, shielding gas supply, and the workpiece. The power source generates the high-frequency current necessary to initiate and stabilize the arc, while the torch holds the tungsten electrode and directs the welding process. Shielding gas, such as argon or helium, is utilized to protect the weld pool from atmospheric contamination, ensuring high-quality, clean welds.
The high-frequency TIG welding process operates based on the principle of controlled heat input. By precisely regulating the current and voltage, welders can achieve accurate control over the heat-affected zone, preventing distortion and ensuring superior weld quality. Furthermore, the non-consumable tungsten electrode enables precise and intricate welding, making it an ideal choice for applications that demand high precision and aesthetic appeal.
III. Advantages of High-Frequency TIG Welding
High-frequency TIG welding offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred choice for various industrial applications. Some of the key benefits include:
High Precision: The precise control over the welding parameters enables operators to achieve intricate welds with minimal heat distortion, ensuring superior joint integrity and aesthetic appeal.
Enhanced Weld Quality: The use of high-frequency current results in a stable arc formation, minimizing the risk of defects such as porosity, cracks, and inclusions, thus ensuring high-quality, reliable welds.
Versatility: High-frequency TIG welding is compatible with a wide range of materials, including exotic metals and alloys, making it a versatile choice for diverse industrial applications.
Minimal Post-Weld Cleanup: The process generates clean, spatter-free welds, reducing the need for extensive post-weld cleaning, thereby saving time and resources during the fabrication process.
Reduced Heat Affected Zone (HAZ): The precise heat control minimizes the size of the heat-affected zone, preventing material distortion and preserving the mechanical properties of the base metal.
Learn Welding Tips: 6 Secrets of Beautiful TIG Welding.
IV. Applications of High-Frequency TIG Welding
The versatility and superior weld quality of high-frequency TIG welding have led to its widespread adoption across various industries. Some notable applications include:
Aerospace Industry: High-frequency TIG welding finds extensive use in the aerospace sector for fabricating critical components such as aircraft frames, engine parts, and fuel systems, where precision and high structural integrity are paramount.
Automotive Manufacturing: The automotive industry utilizes high-frequency TIG welding for the production of exhaust systems, chassis components, and body panels, ensuring robust and durable welds that can withstand harsh operating conditions.
Power Generation Sector: This welding technique is instrumental in the fabrication of power plant components, including turbines, heat exchangers, and nuclear reactor vessels, where the weld quality directly influences the overall efficiency and safety of the systems.
V. Future Trends and Developments
As technology continues to advance, the field of high-frequency TIG welding is expected to witness further innovations and developments. Researchers and manufacturers are continually exploring new techniques and materials to enhance the efficiency, precision, and applicability of this welding process. Moreover, the integration of automation and robotics in high-frequency TIG welding systems is poised to revolutionize the manufacturing landscape, enabling faster production rates and greater consistency in weld quality.
VI. Conclusion
High-frequency TIG welding has emerged as a leading welding technology, offering exceptional precision, versatility, and weld quality across various industries. With its ability to produce clean, robust welds with minimal distortion, this advanced welding process continues to play a pivotal role in the fabrication of critical components and structures. As research and development in this field progress, the applications of high-frequency TIG welding are expected to expand further, revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape and contributing to the advancement of numerous industries.
Related articles:
1. Mastering Shielding Gas in TIG Welding: A Guide to Better Welds
2. TIG Welding Technique Principle, Applications and Considerations
3. A Guide to Heavy Industrial TIG Welding Tools & Equipment
4. How To Setup A TIG Welding Machine For the First Use?
5. Mastering TIG Welding Polarity: PRO Tips for Perfect Welds




