In today’s fast-changing manufacturing landscape, deciding when to adopt laser welding can make a big difference in cost, quality, and throughput. This article explains what laser welding is, what it brings compared to traditional welding, and most importantly: when it makes sense to choose it for your operation.
I. What is Laser Welding and How Does It Work?
Laser welding (also referred to as laser beam welding) is a fusion welding process in which a laser provides the heat source to melt and join materials.

1) Basic principle
-
A laser beam is generated, then delivered (via optics or fibre) and directed onto the joint zone of the work-pieces.
-
The material at the joint melts (and sometimes vaporises) creating a molten pool which, when cooled, solidifies into a joint.
-
Because the laser can apply very high energy density to a narrow spot, the heat-affected zone (HAZ) is often much smaller than in traditional arc or resistance welding.
2) Two key modes
Laser welding can generally operate in two main modes, each suited to different material thicknesses or weld geometries:
-
Conduction mode – lower laser power; heat is delivered to the surface and then conducted into the material. Weld penetration is relatively shallow; good for thin materials or when aesthetics are important.
-
Keyhole (or penetration) mode – higher power density; the laser creates a “keyhole” (vaporised cavity) in the material, enabling deeper, narrower welds often at high speed.
3) Why it matters
Because of the focused energy and narrow HAZ, laser welding offers advantages in terms of precision, minimal distortion, speed (in suitable applications), and the ability to weld challenging materials or joints. These characteristics set the stage for deciding when it makes sense to choose laser welding.
II. Advantages of Laser Welding: Why it Can Be a Good Fit
Before diving into “when you should choose it”, let’s summarise what you gain when laser welding is used in a suitable scenario.
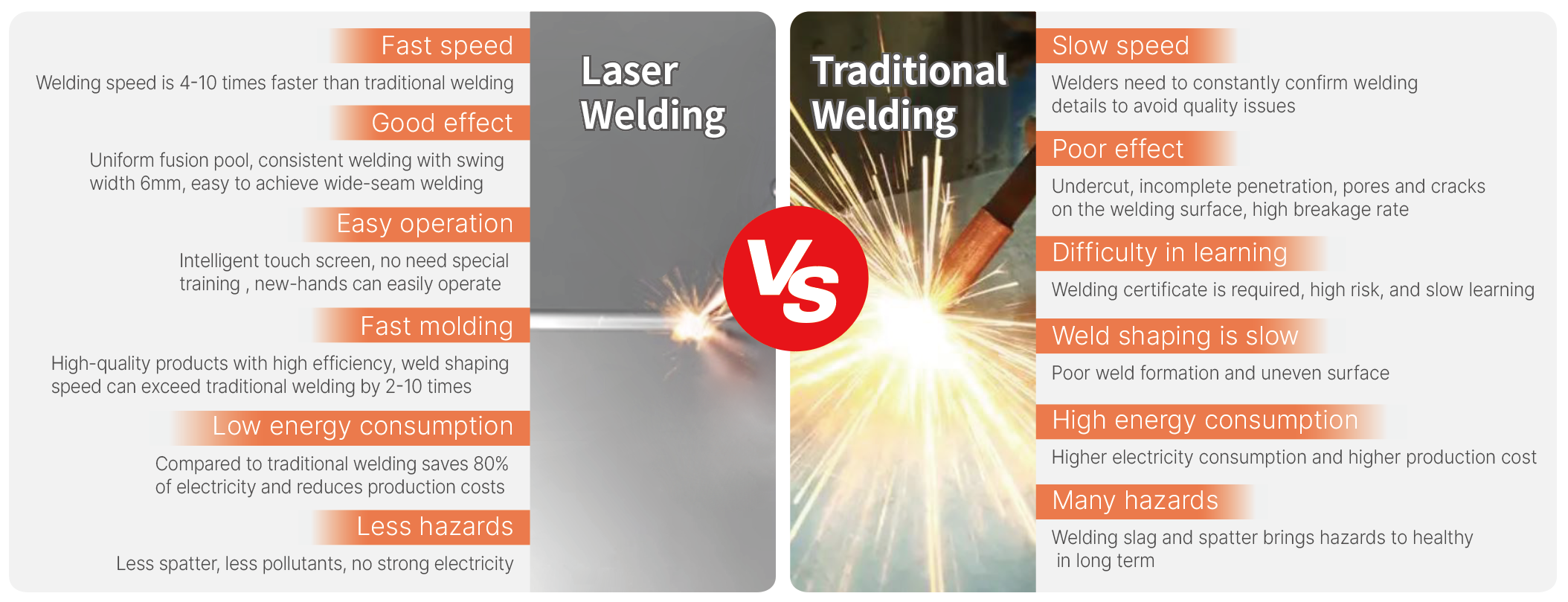
Key benefits
-
Minimal heat-affected zone & low distortion: The concentrated beam limits heating of surrounding material, which reduces warping or deformation.
-
High precision / clean welds: Because the beam is narrow and well-focused, welds can be fine, neat, and suit applications with aesthetic or tight-tolerance demands.
-
High speed (in many cases): For the right materials and geometries, travel speeds can be significantly faster than traditional welding.
-
Suitability for automation & integration: Laser welding systems can be robotic or semi-automatic, making them well-suited to modern production lines.
-
Ability to weld dissimilar materials or thin/complex parts: With the right set-up and parameters, laser welding can join combinations or thin parts that may be challenging for conventional methods.
-
Reduced post-weld finishing: Because the weld bead and heat input are controlled, less grinding or rework is often required.
These advantages suggest that when your application lines up with these strengths, laser welding may offer meaningful performance or cost benefits.
III. When Should You Consider Choosing Laser Welding?
Here we focus on the conditions and decision-points that indicate “yes, this is a good time to choose laser welding for your operation”.
1) High-volume production or high throughput demands
-
If your operation welds many parts with similar geometry and you need speed and consistency, laser welding can make a strong case. For example:
-
In sheet-metal production, where joints are repetitive and speed matters, laser welding can out-perform slower arc processes.
-
In automated lines where robots or fixed cells are used, laser welding integrates well and can reduce cycle time.
2) Thin materials or parts that are heat-sensitive
If you are working with thin gauge metals (sheet steel, aluminium) or components where distortion would compromise fit or finish, laser welding is attractive because of its low heat input and narrow HAZ.
3) Cosmetic or high-precision welds
-
When the weld is visible, or tight dimensional/control tolerances apply (for instance, electronics, medical devices, luxury goods), the precision of laser welding can justify its selection. For example:
-
Welding miniature electronics or micro‐components.
-
Joining materials where weld appearance is critical and minimal distortion is required.
4) Dissimilar materials or challenging joints
-
When you need to weld metals or other materials that are difficult for conventional methods (e.g., aluminium to stainless steel, copper alloys, thin clad combinations), laser welding may offer the capability to do so (with correct set-up).
5) Automation, robotics or work-cell integration
-
If your operation is moving toward or already uses automation/robotics, choosing laser welding now can align with that strategy: it supports robotic beam delivery, offers repeatability, and can reduce reliance on skilled manual welders.
6) When post-weld finishing costs or rework are major factors
-
If your current process requires heavy grinding, touch-up or significant rework due to weld bead size, distortion or thermal damage, then the cleaner results from laser welding might reduce secondary costs and justify the switch.
IV. Practical Considerations & Limitations: When Laser Welding May Not Be the Best Fit
Choosing laser welding isn’t just about the “good fit” scenarios — you must also consider the trade-offs and whether your operation can support them.
1) Up-front investment & cost
-
Laser welding equipment typically has higher capital cost compared to many conventional welding systems. Also, depending on complexity, you may need fixtures, beam delivery systems, automation, safety enclosures. As noted: initial cost is a disadvantage in some cases.
2) Material thickness/penetration limitations
3) Fit-up and joint preparation sensitivity
-
Because laser welding often uses narrow fusion zones and minimal filler, it tends to require better joint fit-up, surface preparation, and cleanliness. Poor fit-up or contamination can lead to defects.
4) Skilled operators and process control
-
Although automation helps, laser welding still requires good process design, control of parameters (power, speed, focus), and possibly higher operator/maintenance skills. Mistakes or misalignment can increase scrap.
5) Safety and setup environment
-
Laser beams are high-energy and optical safety (eye protection, enclosures) is required. Also, the system may require shielding gas, beam delivery optics, and environmental controls.
6) Return on investment timeline
-
Because of the higher up-front cost, you should assess how many parts or what production volume you’ll need to amortise the investment. If your volumes are low or variant-heavy, the benefit may not outweigh cost.
V. A Decision-Checklist: Is Laser Welding Right for Your Operation?
Here’s a practical list you can run through to help decide whether to adopt laser welding:
-
What is your annual volume or weld count for the targeted joint? High volumes favour the investment.
-
What is the material type and thickness? Thin sheets or heat-sensitive materials lean toward laser; very thick or highly mismatched joints may be less suitable.
-
Is the joint geometrically complex, requiring precision or minimal distortion? If yes, laser is a strong contender.
-
What is the current cost of distortion, rework, finishing, scrap or slow cycle time? If these are significant, laser might pay off.
-
Do you have or plan automation/robotic integration? If yes, laser welding aligns well.
-
How good is your joint fit-up, fixturing and surface preparation currently? If your operation can support tight tolerance and cleanliness, laser will perform well; if not, the extra preparation may negate benefits.
-
What is your budget and return-on-investment (ROI) tolerance? Can you commit capital now and wait for payoff via productivity gains?
-
What is the flexibility requirement? If your welds change often or you do many different weld joints, traditional methods may remain more flexible.
-
Do you have or can you access the operator/maintenance skills required? Consider training and process development costs.
-
What is the competitive or quality advantage in your market? If high precision, minimal visible welds or advanced materials are being demanded, laser may give a market edge.
VI. Example Applications Where Laser Welding Works Well
From industry-data and case studies, here are some typical applications where laser welding is already being adopted — giving you a sense of where your own operation might be similar:

-
Automotive: Body panels, chassis joints, powertrain components — where speed and precision matter.
-
Aerospace: Lightweight structures, fuel tanks, where minimal distortion, material performance and high integrity are required.
-
Medical & electronics: Extremely small, delicate parts (implants, microscale welds) where precision and minimal heat damage matter.
-
General metal fabrication: Particularly for thin, high‐quality sheet metal assemblies where finishing and aesthetic are important.
If your operation falls into one of these categories (or similar), laser welding is likely to be one of the strong options to evaluate.
Conclusion
In short: choose laser welding when your operation demands high precision, minimal distortion, good aesthetics, high throughput for comparable joints, and you are prepared (both financially and operationally) to support the required equipment, training and process integration. If your production is low volume, widely variant, or uses thick sections where speed is less critical, or your budget is highly constrained, then conventional welding may remain the more practical choice.
In the evolving industrial landscape, laser welding is becoming more accessible and cost-effective — meaning for many manufacturers it is no longer “just for niche specialists”. The key is to perform a careful assessment of your operation’s specific needs, volumes, materials, joint types and constraints, and compare direct and indirect costs (capital, consumables, finishing, reject rates, distortion, labour) before deciding.
Related articles:
1. Anti-Freeze Tips for Handheld Fiber Laser Welder
2. Laser Welding, Laser Cutting, Laser Drilling, Laser Marking Basics
3. Prices of All Types of Laser Welding Machines for Reference
4. Solutions to Oil Leakage in Pipeline Continuous Laser Welding
5. 5-Step Laser Welding Process: How Does It Work?






