Welding is an art and a science, but sometimes things go wrong, and defects appear on the surface or inside, making the weld weak or strong. Some defects are caused by human error, others by material or machine, but all defects can be fixed or avoided with proper technique and routine. In this article, Megmeet will explore common welding defects, their causes, and easy solutions to help you achieve superior welding quality in 2023 and beyond.
I. Common welding defects:
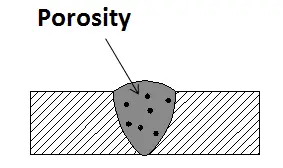
1) Porosity
Description: Porosity appears as small cavities or holes within the weld bead. It occurs due to the entrapment of gas (often hydrogen) during the welding process.
Consequences: Reduced weld strength, susceptibility to cracking, and compromised integrity.
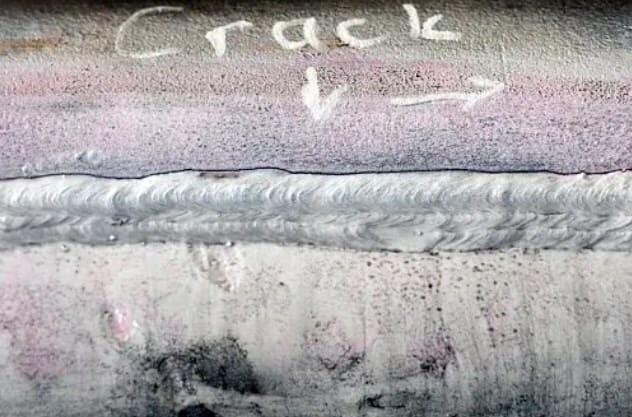
2) Weld Cracks
Description: Weld cracks can be either hot or cold. Hot cracks occur during solidification, while cold cracks develop after the weld has cooled. Cracks can vary in size and location.
Consequences: Cracks weaken the weld, leading to structural instability and potential failure.

3) Incomplete Penetration
Description: Incomplete penetration occurs when the weld does not fully penetrate the joint, leaving a gap or void between the weld and the base material.
Consequences: Reduced joint strength and inadequate fusion, compromising structural integrity.
4) Weld Spatter
Description: Weld spatter consists of small, molten metal droplets that splatter and adhere to the surrounding surfaces during welding.
Consequences: Reduced aesthetics, increased cleanup efforts, and potential interference with adjacent components.
5) Undercutting
Description: Undercutting is a groove or depression along the edges of the weld bead, often due to excessive heat or improper technique.
Consequences: Reduced joint strength, increased stress concentration, and susceptibility to cracking.

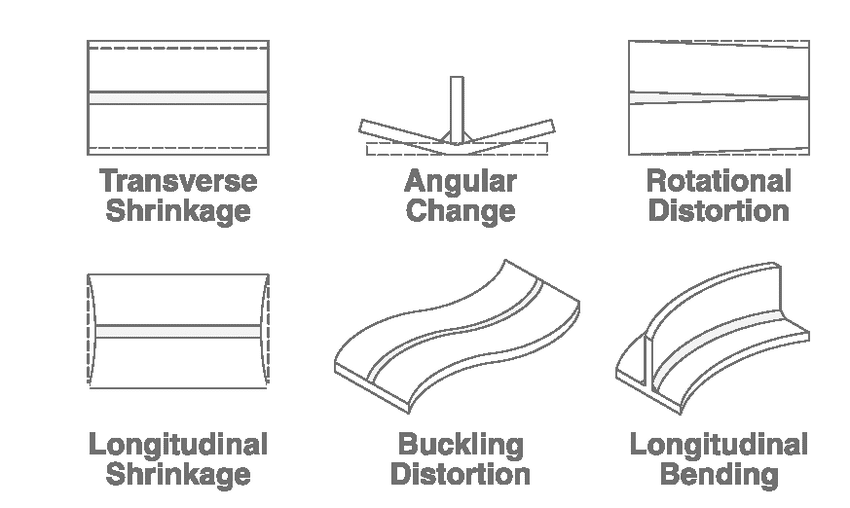
6) Distortion
Description: Welding-induced distortion results in the warping or bending of the welded components due to heat and contraction.
Consequences: Impaired fit and alignment, affecting the overall product's dimensions and functionality.
II. Causes of Welding Defects
Each defect has its cause and effect, and its solution as well. Some require rework or repair or removal, others need adjustment or control or skill. Before knowing how to solve the welding defects, we should first grasp the causes of each welding defect:
Improper Welding Parameters: Incorrect settings for welding current, voltage, travel speed, and electrode type can lead to various defects.
Poor Welding Technique: Inconsistent or incorrect welding techniques, such as incorrect electrode angle or travel speed, can contribute to defects.
Inadequate Material Preparation: Dirty or contaminated base metal, incorrect joint geometry, and inadequate preheating can cause welding defects.
Environmental Factors: Factors such as wind, humidity, and temperature can affect the welding process and lead to defects.
III. Preventive Measures for Welding Defects
Welding defects are not inevitable, they can be prevented or reduced by following the best practices and standards and learning from the experienced and skilled.
1) Proper Welding Technique
Training: Proper training and certification for welders ensure they have the skills and knowledge to perform quality welds.
Quality Control: Implement strict quality control procedures to catch defects early in the welding process.
2) Material Preparation
Cleanliness: Thoroughly clean and degrease base metals to prevent contamination.
Joint Preparation: Ensure correct joint geometry, edge preparation, and fit-up.
Preheating: Preheat the base metal when welding thick materials to reduce the risk of cracking.
3) Welding Environment
Shielding Gas: Use the appropriate shielding gas and ensure proper gas flow to protect the weld from contamination.
Wind Protection: Shield the welding area from wind and drafts to prevent spatter and other defects.
4) Equipment Maintenance
Regular Inspection: Perform regular maintenance and inspections of welding machines, electrodes, and other equipment.
Calibration: Calibrate equipment to ensure it operates at the correct settings.
5) Easy Solutions for Welding Defects
Porosity: Use the correct shielding gas, clean the base metal, and reduce travel speed to minimize porosity.
Weld Cracks: Control hydrogen content in the weld metal, ensure proper preheat, and use the correct filler metal.
Lack of Fusion: Adjust welding parameters, maintain proper electrode angle, and ensure good joint fit-up.
Undercutting: Optimize welding current and travel speed, and maintain the correct electrode angle.
Spatter: Adjust welding parameters, such as voltage and wire feed speed, to reduce spatter.
Incomplete Penetration: Increase welding current, reduce travel speed, and ensure proper joint preparation.
Distortion: Use proper welding techniques and consider clamping or fixturing to minimize distortion.
Burn-Through: Reduce welding current and travel speed or use a lower heat input process for thin materials.
Welder's Checklist
Follow welding procedures and standards:
Inspect and clean base metals thoroughly.
Verify proper joint preparation and fit-up.
Ensure correct shielding gas and gas flow rates.
Monitor and adjust welding parameters as needed during the process.
Conduct visual inspections of welds during and after welding.
Implement non-destructive testing (NDT) techniques for critical applications.
Related articles: Top 5 Welding Problems and How to Solve Them: A Comprehensive Guide
IV. Quality Control and Inspection
Welding defects are not insurmountable, they can be detected and corrected by using the appropriate methods and tools, and ensuring the quality and safety of the weld.
1) Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
NDT methods, such as radiographic testing (RT), ultrasonic testing (UT), magnetic particle testing (MT), and dye penetrant testing (PT), can detect defects without damaging the weld.
2) Visual Inspection
Visual inspection involves examining the weld with the naked eye or using tools like magnifying glasses and borescopes to identify defects.
3) Welding Standards and Codes
Adherence to industry-specific welding standards and codes, such as those provided by the American Welding Society (AWS) or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), can help ensure the quality of welds.
Conclusion
Identifying and addressing welding defects is crucial for producing safe and reliable welded structures and components. By understanding the common welding defects and their causes and implementing easy solutions, welders in 2023 can significantly improve the quality of their work. Additionally, preventive measures, proper welding techniques, and adherence to welding standards play key roles in ensuring defect-free welds. Remember, the art of welding involves continuous learning and improvement, and staying up-to-date with the latest welding technologies and best practices is essential for welders of all levels.
Related articles:
1. How to Prevent and Address your Welding Porosity Defect?
2. Common Electrical Welding Machine Defects and Solutions
3. What Are Welding Beads? (types, functions, techniques & defects)
4. Types of Welding Defects in Shipbuilding and Their Remedies
5. How to Identify the 7 Most Dangerous Welding Defects?







