Selecting the optimal welding equipment for the automotive industry is not just about picking the most powerful machine; it’s about making a strategic investment that directly impacts quality, efficiency, safety, and, ultimately, profitability. This decision is far more complex than it may initially appear—it involves a deep understanding of specific welding applications, materials, production volumes, and future industry trends. By carefully evaluating your needs, you can transform your welding operation into a competitive advantage, positioning your business for success in a rapidly evolving market.
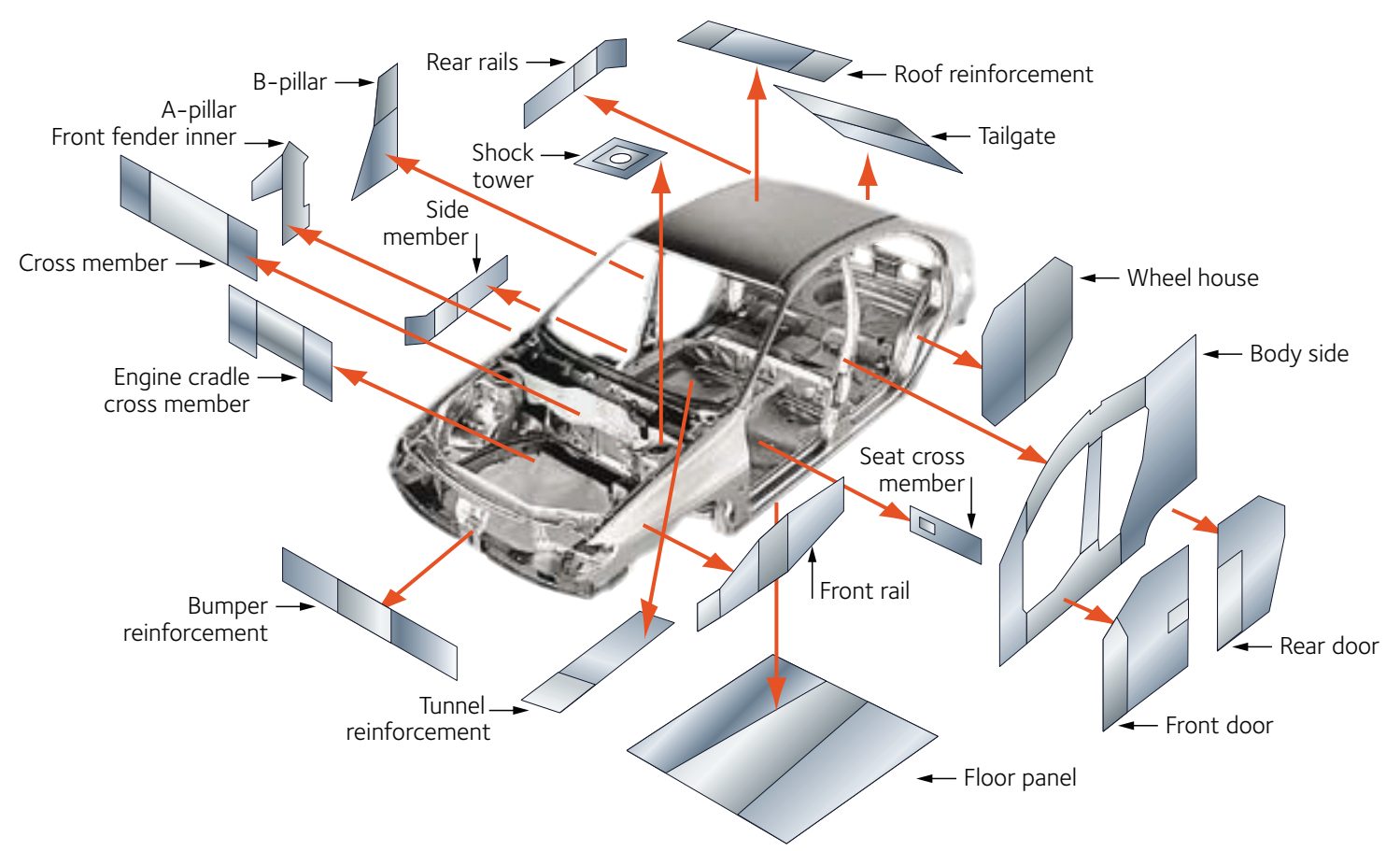
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll help you navigate the complexities of choosing the right welding equipment for automotive applications, ensuring you make an informed, strategic decision that aligns with both immediate requirements and long-term goals.
I. Pinpoint Your Automotive Application & Operational Demands:
The first and most critical step in selecting welding equipment is understanding the specific demands of your operation. It’s not enough to simply look at the materials you will be welding—it's also important to define your application needs and align them with the strategic vision for your business.
1. Collision Repair & Restoration (Body Shops):
When it comes to collision repair and restoration, precision is paramount. Repairing or restoring vehicles requires minimal heat distortion, particularly for thin gauge metals (0.6mm - 1.5mm), while ensuring durability and aesthetic finish. Additionally, replicating OEM spot weld patterns and material properties is crucial for safety and structural integrity.

Key Materials:
Mild steel, High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) steels
Ultra High-Strength Steels (UHSS), Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS)
Aluminum alloys
Key Considerations:
To achieve the best results, an inverter-based Resistance Spot Welder (RSW) with advanced control is recommended. This equipment ensures high-quality spot welds on a variety of materials, and Pulse MIG/MAG welders are ideal for working with UHSS/AHSS, allowing controlled heat input to prevent embrittlement. TIG welders may also be used for custom work or visible aesthetic welds on classic restorations or aluminum.
Strategic Angle:
2. Custom Fabrication & Performance Tuning:
For shops involved in custom fabrication or performance tuning, the focus shifts to high-quality, visually appealing welds. Custom exhaust manifolds, suspension components, and turbo piping require precise control to achieve intricate designs, and material integrity is key.
Key Materials:
Stainless steel (304, 316), Aluminum (6061, 3003)
Chromoly (4130), Titanium
Key Considerations:
Advanced AC/DC TIG welders with high-frequency start and adjustable AC balance/frequency are essential for handling various materials and thicknesses. These features allow fine-tuning for materials like stainless and aluminum, ensuring that you prevent sugaring on stainless and excessive grain growth in aluminum. High-quality orbital welding solutions may also be considered for repetitive, complex pipe joints.
Strategic Angle:
3. OEM Production Lines & Component Manufacturing:
For mass production and component manufacturing, efficiency and repeatability are the keys to success. The focus is on minimizing cycle times, ensuring defect prevention, and integrating seamlessly with Industry 4.0 technologies.

Key Materials:
High volumes of mild steel, HSLA, UHSS, AHSS, and aluminum
Emerging multi-material joining strategies
Key Considerations:
Robotic MIG/MAG welding (Pulse, Double Pulse) offers precise control and repeatability for automated production lines. Automated Resistance Spot Welding (RSW) with force and current monitoring ensures consistent quality, while Laser Welding (Fiber or CO2) offers precision, speed, and adaptability for advanced materials. Additionally, Friction Stir Welding (FSW) is ideal for specific aluminum applications where traditional methods may fail.
Strategic Angle:
For OEM production, invest in highly automated, intelligent welding systems that maximize throughput, reduce downtime, and integrate predictive maintenance capabilities. This investment supports scalable operations, which is crucial for meeting increasing production demands.
4. Heavy Duty & Commercial Vehicle Manufacturing (Trucks, Buses, Trailers):
In heavy-duty manufacturing, the emphasis is on structural integrity and durability. High deposition rates and deep penetration are critical when working with thicker materials, ensuring that the finished product can withstand extreme operating conditions.
.jpg)
Key Materials:
Key Considerations:
High-amperage MIG/MAG welders (500A+) with pulse or double pulse functions are essential for ensuring penetration on thick materials. For extreme deposition rates, Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is ideal, especially for out-of-position welds. Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) is often used for long, straight seams on thick plates.
Strategic Angle:
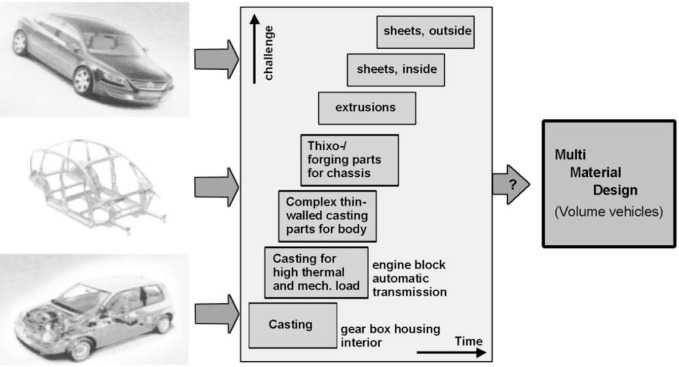
II. Mastering the Arc: Advanced Welding Processes and Emerging Technologies:
As welding technologies continue to advance, it's essential to stay informed about the latest developments that can improve your operations. Beyond traditional methods, consider these emerging technologies and their impact on your operations:
Advancements in MIG welding include Cold Metal Transfer (Fronius CMT or Megmeet RDT) and Low Heat Input MIG processes, which are ideal for working with thin materials, gap bridging, and MIG brazing of galvanized steels. High-speed MIG processes push productivity limits, and intelligent MIG systems now automatically adjust parameters in real-time for optimal weld quality.
Digital TIG power sources provide precise control over every aspect of the waveform, allowing for superior repeatability and data logging. These advancements are particularly beneficial for applications requiring high-quality, aesthetically pleasing welds on materials like stainless steel and aluminum.
3. Resistance Spot Welding (RSW): Smarter, Stronger, Greener
Inverter-based RSW provides precise control over weld parameters, essential for working with advanced materials like AHSS/UHSS. Adaptive control systems automatically adjust settings to account for material stack-up, ensuring a more consistent and energy-efficient weld.
Fiber lasers offer smaller spot sizes, higher efficiency, and greater flexibility, making them ideal for high-speed, precise welding applications. Hybrid Laser-MIG/MAG welding combines the advantages of laser with the deposition rate of arc welding, particularly useful for joining advanced materials.
5. Friction Stir Welding (FSW): Solid-State Joining
This process, which generates heat through friction, offers superior mechanical properties for aluminum joints compared to traditional fusion welding methods. It’s particularly useful in the automotive industry for lightweighting and joining aluminum alloys, critical for electric vehicles (EVs).
III. Material Science & Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS)/UHSS:
The growing use of AHSS/UHSS in automotive manufacturing requires a more intelligent approach to welding. These materials offer enhanced crashworthiness and lightweighting but are highly sensitive to heat.

Key Considerations:
Heat Input Control: AHSS/UHSS materials can suffer from embrittlement if exposed to excessive heat, so low heat input welding processes are non-negotiable.
Filler Metal Selection: Specific filler metals are often required to match the mechanical properties of the base material.
OEM Procedures: Adhering to OEM repair guidelines is crucial to maintaining the structural integrity of vehicles and ensuring safety compliance.
IV. Key Equipment Features & Specifications
When choosing welding equipment, it’s essential to go beyond basic features and look at advanced specifications that can optimize your operation’s efficiency and quality.
1. Power Output and Usable Range:
While most welders will specify their maximum amperage, the usable amperage range is often more important. A welder may have a peak output of 500A, but its ability to perform at lower amperages (e.g., 50-100A) is crucial for tasks such as welding thin materials or delicate components. A machine that offers smooth, stable performance across a wider amperage range will provide versatility and consistent results.
2. Duty Cycle and Continuous Operation:
The duty cycle, expressed as a percentage, indicates how long a welder can run before it needs to cool down. Machines with a higher duty cycle (80-100%) are suitable for continuous, high-volume production environments. For occasional or low-volume jobs, a machine with a lower duty cycle may suffice, but for high-demand scenarios, high-durability machines with extended duty cycles ensure uptime and reduce the frequency of interruptions for cooling.
3. Advanced Control Systems:
Modern welders feature digital control systems that offer precise settings adjustments for voltage, wire feed speed, and heat input, among others. These controls can improve weld quality, reduce defects, and minimize the time required to set up each weld. User-friendly interfaces allow operators to quickly adjust settings, leading to more efficient production.
4. Data Feedback and Monitoring:
Many advanced welders now come with real-time monitoring systems that track critical data like arc stability, voltage, and current. These systems allow operators to quickly troubleshoot any issues and make adjustments on the fly. Additionally, data logging features help monitor long-term performance trends, ensuring that the machine remains within optimal parameters.
5. Consumables Management:
High-quality welding equipment also comes with automated systems for consumables management. These systems automatically adjust for wire feed speed and gas flow, reducing downtime and increasing operational efficiency. By ensuring that consumables are used effectively, these systems extend the lifespan of both consumables and the machine itself.
V. Automation & Integration: The Smart Factory Ecosystem
As manufacturing moves toward Industry 4.0, the integration of automation into welding operations becomes essential for maximizing efficiency and competitiveness.

1. Seamless Digital Connectivity:
Modern welding systems are designed to integrate with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) or Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. This integration allows for real-time data exchange, enabling monitoring of key performance metrics, such as welding time, quality control, and material usage. Manufacturers can instantly detect anomalies and adjust the process accordingly.
2. Collaborative Robots (Cobots):
Cobots, or collaborative robots, work alongside human operators to enhance productivity and safety. These robots are adaptable and can perform repetitive tasks like loading/unloading materials or holding welding torches. Cobots improve production efficiency by reducing operator fatigue and enhancing the overall precision of welding tasks.
3. Adaptive Vision Systems:
Vision systems equipped with AI-powered defect detection and seam tracking capabilities ensure that each weld is of the highest quality. These systems automatically detect imperfections such as porosity or undercuts, allowing for real-time corrections and reducing the need for manual inspections. Vision systems can also guide robotic welders to follow complex geometries with precision.
4. Software and Simulation Tools:
Welding robots and automation equipment now come with offline programming software, which allows operators to simulate welding paths, optimize parameters, and troubleshoot potential issues before production begins. This software reduces setup time, enhances precision, and minimizes errors in the final product.
5. Integrated Maintenance and Analytics:
Predictive maintenance capabilities are another hallmark of smart welding systems. By constantly monitoring key machine health indicators, these systems can predict when maintenance is needed, helping prevent unplanned downtime and extending equipment life. With integrated analytics, manufacturers can improve performance, identify potential issues before they become problems, and optimize the entire production process.
VI. The "Total Cost of Ownership" (TCO):
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) goes beyond the initial purchase price and considers all the associated costs over the lifecycle of the welding equipment. By evaluating TCO, you ensure that the equipment delivers long-term value and meets your operational goals.
1. Upfront Cost vs. Long-term Savings:
The initial purchase price is just one part of the equation. High-quality equipment that comes with advanced features such as energy efficiency, low maintenance, and extended duty cycles can save significant amounts in operational costs over time. It’s often worth investing in machines with higher upfront costs if they result in greater operational savings, fewer defects, and less frequent repairs.
2. Energy Efficiency:
3. Maintenance and Downtime:
Frequent repairs and maintenance can add substantial costs to a welding operation. Machines with predictive maintenance capabilities reduce downtime by monitoring equipment health in real-time. Regular maintenance ensures machines remain in optimal condition, reducing the risk of unexpected breakdowns and enhancing the machine’s long-term durability.
4. Consumables and Material Costs:
Consumables such as filler wires, electrodes, and shielding gases are ongoing expenses that impact TCO. High-quality machines designed for efficient use of consumables can help lower these costs over time. Additionally, reducing scrap and rework through improved weld quality leads to significant savings on material costs.
5. Training and Skill Development:
While the cost of operator training is often overlooked, it is an essential factor in TCO. Proper training ensures that equipment is used effectively, reducing human error and enhancing machine efficiency. Certified training programs help operators and maintenance staff work at peak efficiency, minimizing errors and reducing costly rework.
VII. Strategic Partnerships & Vendor Relationships: More Than Just a Supplier
In today’s competitive landscape, welding equipment vendors should be viewed as strategic partners rather than simple suppliers. A strong partnership provides valuable support in optimizing operations and ensuring long-term success.
1. Application Engineering Support:
A good vendor offers application engineering support, helping you optimize the welding process for specific materials, geometries, or production requirements. Their expertise ensures that you are using the most appropriate equipment and parameters for each job, improving the quality and efficiency of your welding operations.
2. Training and Certification Programs:
Many top-tier vendors provide training and certification programs for both operators and maintenance staff. These programs ensure that your team is equipped with the necessary skills to operate and maintain advanced equipment effectively. Well-trained staff can help reduce errors, improve productivity, and maintain high-quality standards throughout production.
3. Research and Development (R&D) Collaboration:
A vendor that is committed to research and development will work with you to address future challenges in welding technology, such as multi-material joining, advanced automation, and even electric vehicle (EV) battery production. Staying ahead of technological trends ensures your operation remains competitive and capable of handling emerging market demands.
4. Global Support and Service:
For multinational operations, a vendor offering global support is essential. Reliable service across different regions ensures that equipment is well-maintained and issues are resolved quickly, minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent production quality across your facilities.
5. Long-term Partnership:
Choosing a vendor with a long-term vision helps ensure that you stay at the forefront of technology and market trends. A strong partnership also enables access to upgrades, new equipment releases, and a continuous feedback loop, helping you improve your processes over time.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right welding equipment for the automotive industry is a multifaceted decision that requires careful evaluation of your specific needs and future growth. By considering the factors outlined in this guide, automotive manufacturers can make informed choices that will drive efficiency, quality, and profitability, ensuring they stay competitive in an increasingly complex and fast-moving industry.
Related articles:
1. 3 Easy Ways to Adjust Your Welding Machine
2. 2023 Top 5 Rated Laser Welders & Welding Machines for Sale
3. Powerful Heavy Duty Inverter Welding Machines For Precision Welding
4. Top 10 Handheld Laser Welding Machine Brands of 2023
5. How Much Power is Consumed by a 3 Phase Welding Machine?






.jpg)



