Welding is a fundamental process in various industries, from construction and manufacturing to automotive and aerospace. To achieve quality welds consistently, welders rely on specialized equipment, including welding machines. One crucial aspect of welding machine performance is its duty cycle. In this article, Megmeet-welding will explore what the duty cycle is in welding, its significance, how to calculate it, and the factors affecting it.
.jpg)
I. Basics of Duty Cycle
1) Definition and Concept
Duty cycle is a critical specification associated with welding machines. It represents the percentage of time a welding machine can operate continuously within a specific time frame, typically a 10-minute period, before requiring a cool-down period. In simple terms, it indicates how long a welding machine can be actively used within a given cycle without overheating or damaging the equipment.
Duty cycle is expressed as a percentage. For example, if a welding machine has a duty cycle of 60% at a specific amperage, it means the machine can weld for six minutes out of every ten-minute interval without overheating. The remaining four minutes are reserved for the machine to cool down.
2) Duty Cycle Rating
Welding machines come with different duty cycle ratings, and these ratings vary based on factors such as the machine's size, design, and intended use. Higher-end industrial machines typically have higher duty cycle ratings compared to smaller, portable units.
The duty cycle rating is often specified at a particular welding current or amperage. This is because the duty cycle can vary depending on the welding machine's output. For instance, a welding machine may have a 60% duty cycle at 200 amps, but the duty cycle may differ at other amperage settings.
II. Factors Affecting Duty Cycle
Several factors influence the duty cycle of a welding machine. Understanding these factors is essential for welders to make informed decisions when selecting a welding machine and optimizing its performance.
1) Ambient Temperature
Ambient temperature plays a significant role in determining a welding machine's duty cycle. Higher ambient temperatures can cause the machine to heat up more quickly, reducing the available welding time before it needs to cool down. Conversely, lower ambient temperatures can extend the duty cycle.
2) Welding Current
The welding current or amperage setting has a direct impact on the duty cycle. In general, higher welding currents generate more heat, which can shorten the available welding time within a cycle. Lower current settings result in less heat production and a longer duty cycle.
3) Duty Cycle and Electrode Size
The size and type of electrode being used also influence the duty cycle. Larger electrodes or those with higher current-carrying capacities generate more heat during welding. This can decrease the duty cycle compared to using smaller electrodes.
4) Welding Machine Cooling Systems
The design and effectiveness of a welding machine's cooling system play a crucial role in duty cycle performance. Welding machines with advanced cooling systems, such as fans or liquid cooling, can dissipate heat more efficiently, allowing for longer continuous operation.
III. Calculating Duty Cycle
1) Duty Cycle Formula
The duty cycle percentage can be calculated using the following formula:
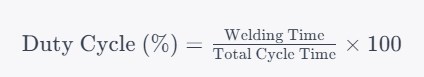
Where:
Welding Time is the duration the welding machine can operate continuously before requiring a cool-down period.
Total Cycle Time is the specified time frame, typically 10 minutes, during which the duty cycle is measured.
2) Example Calculation
Let's say you have a welding machine with a duty cycle of 40% at 250 amps. This means the machine can weld for 4 minutes out of every 10-minute cycle.
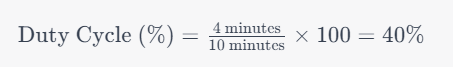
This calculation indicates that the machine can operate at 250 amps continuously for 4 minutes before needing a 6-minute cool-down period.
IV. Interpreting Duty Cycle Ratings
1) Common Duty Cycle Ratings
Welding machines come with various duty cycle ratings, and it's important to understand what these ratings mean. Common duty cycle ratings include 20%, 40%, 60%, and 100%. Here's how to interpret them:
20% Duty Cycle: Suitable for light-duty and occasional welding tasks. The machine can operate for 2 minutes within a 10-minute cycle.
40% Duty Cycle: Suitable for general-purpose welding. The machine can operate for 4 minutes within a 10-minute cycle.
60% Duty Cycle: Ideal for medium-duty welding applications. The machine can operate for 6 minutes within a 10-minute cycle.
100% Duty Cycle: Reserved for heavy-duty industrial welding. The machine can operate continuously without requiring a cool-down period.
2) Selecting the Right Welding Machine
When selecting a welding machine, consider the type of welding work you'll be performing and the expected amperage requirements. It's essential to choose a machine with a duty cycle that aligns with your welding needs. Overloading a welding machine beyond its duty cycle can result in overheating, reduced weld quality, and potential damage to the equipment.
V. Extending Duty Cycle
1) Strategies for Maximizing Duty Cycle
Welders can employ several strategies to make the most of a welding machine's duty cycle:
Optimize Current Settings: Use the appropriate welding current setting for the job. Using a lower amperage setting when possible can extend the duty cycle.
Preheat Workpieces: Preheating thick workpieces can reduce the heat input required during welding, potentially allowing for longer welding times within the duty cycle.
Intermittent Welding: If the welding task permits, consider breaking it into shorter segments with rest intervals to allow the welding machine to cool down between welds.
2) Best Practices for Prolonging Welding Machine Life
To ensure the longevity of your welding machine and its consistent performance, follow these best practices:
Proper Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain your welding machine according to the manufacturer's recommendations. This includes cleaning, lubrication, and replacement of worn components.
Clean Work Environment: Keep the work area clean and free of dust, debris, and metal shavings. Blocked cooling systems can lead to overheating.
Quality Electrodes: Use high-quality welding electrodes that match the amperage requirements of your job. Inferior electrodes can lead to more heat generation and a shorter duty cycle.
VI. Importance of Duty Cycle in Welding Applications
1) Impact on Productivity
Understanding and effectively managing the duty cycle is crucial for welding productivity. Choosing a welding machine with an appropriate duty cycle rating ensures that work proceeds smoothly without frequent interruptions for cooling down the equipment. This is particularly important in industrial settings where time is money, and production schedules need to be met.
2) Safety Considerations
Ignoring duty cycle limitations can result in overheating of the welding machine, which can pose safety risks to both the equipment and the welder. Overheating can lead to equipment malfunction, increased chance of accidents, and potential damage to the workpiece. Following duty cycle guidelines is essential for maintaining a safe work environment.
VII. Conclusion
The duty cycle is a fundamental concept in welding that directly impacts the efficiency, safety, and longevity of welding equipment. By understanding duty cycle ratings, calculating them accurately, and considering factors such as ambient temperature and welding current, welders can select the right machine for their needs and optimize its performance.
Properly managing the duty cycle not only enhances productivity but also ensures the safety of welders and the quality of welds. It is a key element in the successful execution of welding projects across a wide range of industries. Whether you're a professional welder or an enthusiast, a solid grasp of the duty cycle is essential for achieving consistent and reliable welding results.
Related articles:
1. Heavy-Duty Welding: How Megmeet-welding Revolutionize It
2. Powerful Heavy Duty Inverter Welding Machines For Precision Welding
3. Heavy Duty Welder Brings Greater Productivity
4. How Welding Technology Drives Manufacturing Industry
5. Revolutionizing Industrial Welding: Discover the Power of Megmeet Welding Technology



.jpg)
