Welding is a critical process in the fabrication of steel structures and components across various industries, from construction to manufacturing. However, like any manufacturing process, welding is not without its challenges. Welding defects can compromise the structural integrity and performance of steel materials, potentially leading to safety hazards and costly rework. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore common welding defects encountered in steel materials and provide practical remedies to ensure high-quality welds.
I. Common Welding Defects in Steel Material
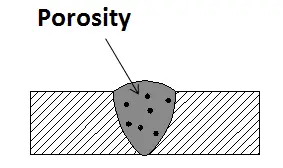
1. Porosity
Porosity is one of the most prevalent welding defects in steel materials. It appears as tiny cavities or voids within the weld bead, often caused by gas entrapment during the welding process. Common sources of porosity include:
Contaminated Base Metal: Steel surfaces must be clean and free from contaminants like oil, rust, or paint before welding. Any contaminants can vaporize and create porosity.
Inadequate Shielding Gas: Proper shielding gas, such as argon or CO2, is essential to protect the weld pool from atmospheric gases. Insufficient gas flow or improper coverage can lead to porosity.
Moisture Content: High moisture content in the welding consumables, such as electrodes or filler wire, can release gas during welding, causing porosity.
2. Incomplete Fusion or Penetration
Incomplete fusion or penetration occurs when the weld metal does not fully bond with the base material. This defect can result in weak and unreliable welds. Causes include:
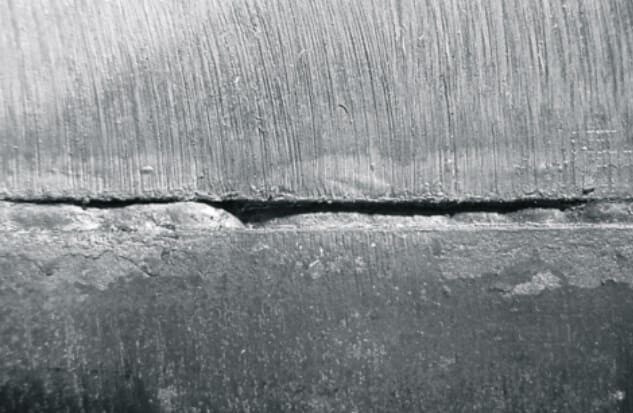

Insufficient Heat: Not providing enough heat during welding can prevent proper fusion. Ensure the welding parameters are set correctly for the steel being used.
Improper Joint Preparation: Joint design and preparation play a crucial role in achieving proper fusion. Inadequate beveling or joint clearance can lead to this defect.
3. Cracking
Cracking in welded steel can take various forms, such as hot cracking, cold cracking, or stress cracking. Cracks compromise the structural integrity of the weld and can lead to catastrophic failure. Common causes include:
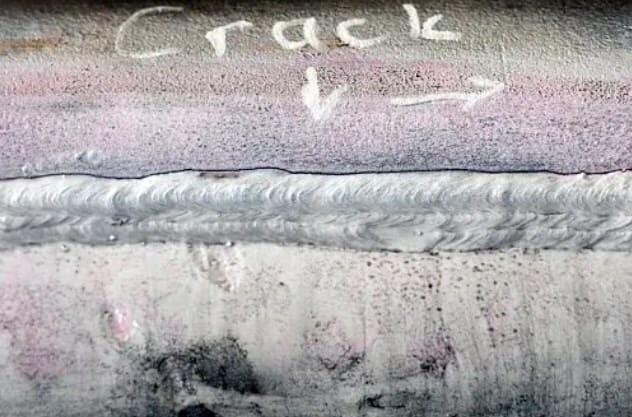

High Residual Stress: Rapid cooling after welding can create high residual stresses in the weld zone, increasing the likelihood of cracking.
Inadequate Preheating: Failure to preheat the steel, especially for thicker sections, can lead to cracking due to thermal stress.
4. Undercutting
Undercutting is a groove-like depression along the weld toe or fusion boundary, often resulting from excessive heat input or incorrect welding technique. It weakens the weld and can serve as a stress concentration point.

5. Weld Spatter
Weld spatter refers to the tiny droplets of molten metal that can land on the surrounding areas during welding. It not only mars the appearance but can also introduce surface irregularities and weaken the steel material.
II. Remedies for Welding Defects in Steel Material
1. Porosity Remedies
Clean the Base Metal: Ensure that the steel surfaces to be welded are thoroughly cleaned and free from contaminants like rust, oil, and paint.
Optimize Shielding Gas: Adjust the shielding gas flow rate and coverage to prevent atmospheric gas infiltration. Use high-purity gases when possible.
Preheat Consumables: Store welding consumables in a dry environment to prevent moisture absorption.
2. Incomplete Fusion or Penetration Remedies
Maintain Proper Heat: Ensure that the welding parameters (amperage, voltage, and travel speed) are set correctly for the steel material and joint configuration.
Proper Joint Preparation: Follow recommended joint design and preparation guidelines, including beveling and joint clearance.
3. Cracking Remedies
Control Cooling Rate: Use methods like post-weld heat treatment or controlled cooling to reduce the risk of cracking, especially in thick sections.
Preheat: Preheat the steel material to a specified temperature before welding, particularly for thicker sections or materials prone to cracking.
4. Undercutting Remedies
5. Weld Spatter Remedies
Use Anti-Spatter Products: Apply anti-spatter sprays or coatings to welding equipment and surfaces to minimize weld spatter adhesion.
Adjust Welding Parameters: Fine-tune welding parameters to minimize spatter formation.
III. How does the Megmeet welding machine avoid welding defects?
Megmeet welding machines are known for their advanced technology and features that help minimize welding defects and ensure high-quality welds. Here are some ways in which Megmeet welding machines can help avoid welding defects:
Precise Welding Parameters: Megmeet welding machines allow precise control over welding parameters such as amperage, voltage, and travel speed. This precision ensures that the correct amount of heat is applied to the weld, reducing the likelihood of defects like incomplete fusion or penetration.
Digital Control Systems: Many Megmeet welding machines feature digital control systems that provide real-time monitoring and adjustment of welding parameters. This helps maintain consistency throughout the welding process, minimizing the risk of defects.
Stable Arc Performance: Megmeet welding machines are designed to provide a stable and consistent arc, which is essential for achieving uniform welds. A stable arc reduces the chances of defects such as undercutting and porosity.
High-Quality Shielding Gas Control: Proper shielding gas is crucial in preventing porosity and ensuring the integrity of the weld. Megmeet welding machines are equipped with reliable gas delivery systems that maintain consistent and adequate gas coverage.
Advanced Pulse Welding Technology: Some Megmeet welding machines offer pulse welding technology, which can help control heat input and reduce the risk of overheating and cracking, particularly in thin materials.
User-Friendly Interfaces: Megmeet welding machines often come with user-friendly interfaces and intuitive controls, making it easier for welders to set and adjust welding parameters accurately.
Quality Construction: Megmeet is known for its durable and well-built welding machines. High-quality construction materials and craftsmanship contribute to the stability and reliability of the equipment, reducing the likelihood of defects due to machine malfunction.
Comprehensive Training and Support: Megmeet provides training and support to welders and technicians to ensure they understand how to use the equipment effectively. Proper training can significantly reduce the risk of welding defects caused by operator error.
Customization Options: Some Megmeet welding machines offer customization options, allowing welders to tailor the equipment's settings to the specific requirements of their welding projects. This flexibility can lead to better weld quality and defect prevention.
Adherence to Industry Standards: Megmeet welding machines are designed to meet or exceed industry standards for welding quality and safety. This commitment to quality assurance helps ensure that the equipment is less prone to defects.
Regular Maintenance and Calibration: Megmeet recommends and guides regular maintenance and calibration of their welding machines. Proper maintenance ensures that the equipment operates at peak performance, reducing the risk of defects.
Conclusion
Welding defects can pose significant challenges in the fabrication of steel materials, affecting both their structural integrity and appearance. However, by understanding the common causes of these defects and implementing the appropriate remedies, welders can achieve high-quality welds that meet the stringent requirements of various industries.
At Megmeet Welding Technology, we prioritize the importance of precision and quality in welding processes. Whether you're working with structural steel, pipelines, or intricate components, using Megmeet high-performance welding machine and following these defect prevention and remediation techniques will help you produce reliable and durable welds. Remember that a commitment to excellence in welding not only ensures the safety of end products but also contributes to the overall efficiency and success of your welding projects.
In addition, you can read Welding Defects, Problems And Easy Solutions [2023] to learn more tips to avoid and respond to welding defects.
Related articles:
1. Common Defects and Faults in Robotic Welding: Causes and Solutions
2. In-Depth Analysis of 8 Common Defects in Submerged Arc Welding
3. How to Prevent and Address your Welding Porosity Defect?
4. Common Electrical Welding Machine Defects and Solutions
5. What Are Welding Beads? (types, functions, techniques & defects)







