As industries race toward automation and smarter production, industrial collaborative robots—or cobots—have become the centerpiece of modern manufacturing. These advanced robots are not just about replacing labor; they’re about working alongside humans, sharing tasks, and improving efficiency, safety, and product quality.
Collaborative robots are lightweight, flexible, and intelligent machines that can be deployed in a wide range of industrial tasks—from assembly and welding to packaging and inspection. Unlike traditional industrial robots that require safety cages and complex programming, cobots can safely interact with human workers and adapt to new tasks with minimal setup time.

In this guide, we’ll explore the top 10 real-world applications of collaborative robots in manufacturing and explain why they’re revolutionizing how factories operate in 2025.
1. Assembly and Component Handling
Assembly is one of the most common areas where collaborative robots shine. Whether it’s mechanical assembly, electronics production, or appliance manufacturing, cobots can handle repetitive, precise, and ergonomically demanding tasks with ease.
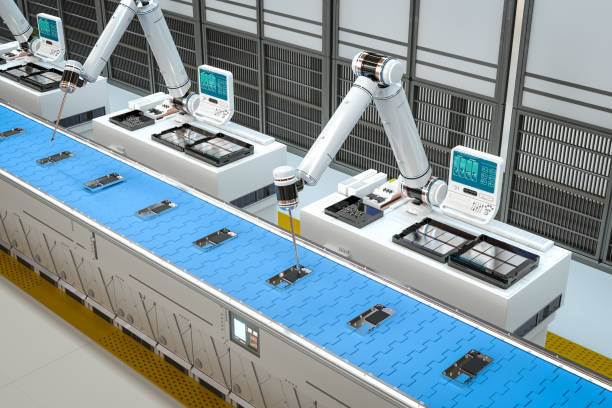
Typical cobot assembly applications include:
Fastening and screwing electronic or mechanical parts
Inserting connectors, plugs, or seals in automotive systems
Press-fitting components with consistent pressure
Performing delicate subassembly work such as circuit board placement
Because cobots can sense force and torque, they can handle delicate materials without causing damage. Their flexibility also means manufacturers can reprogram them quickly for different products or variants, supporting high-mix, low-volume production.
In short, cobots deliver repeatability, speed, and ergonomics—reducing human fatigue while maintaining top-tier precision.
2. Welding and Metal Fabrication
Welding is one of the most demanding industrial processes—and one of the most popular applications for cobots. A collaborative welding robot can perform MIG, TIG, or arc welding with remarkable accuracy, maintaining perfect travel speed and torch angle across every weld seam.
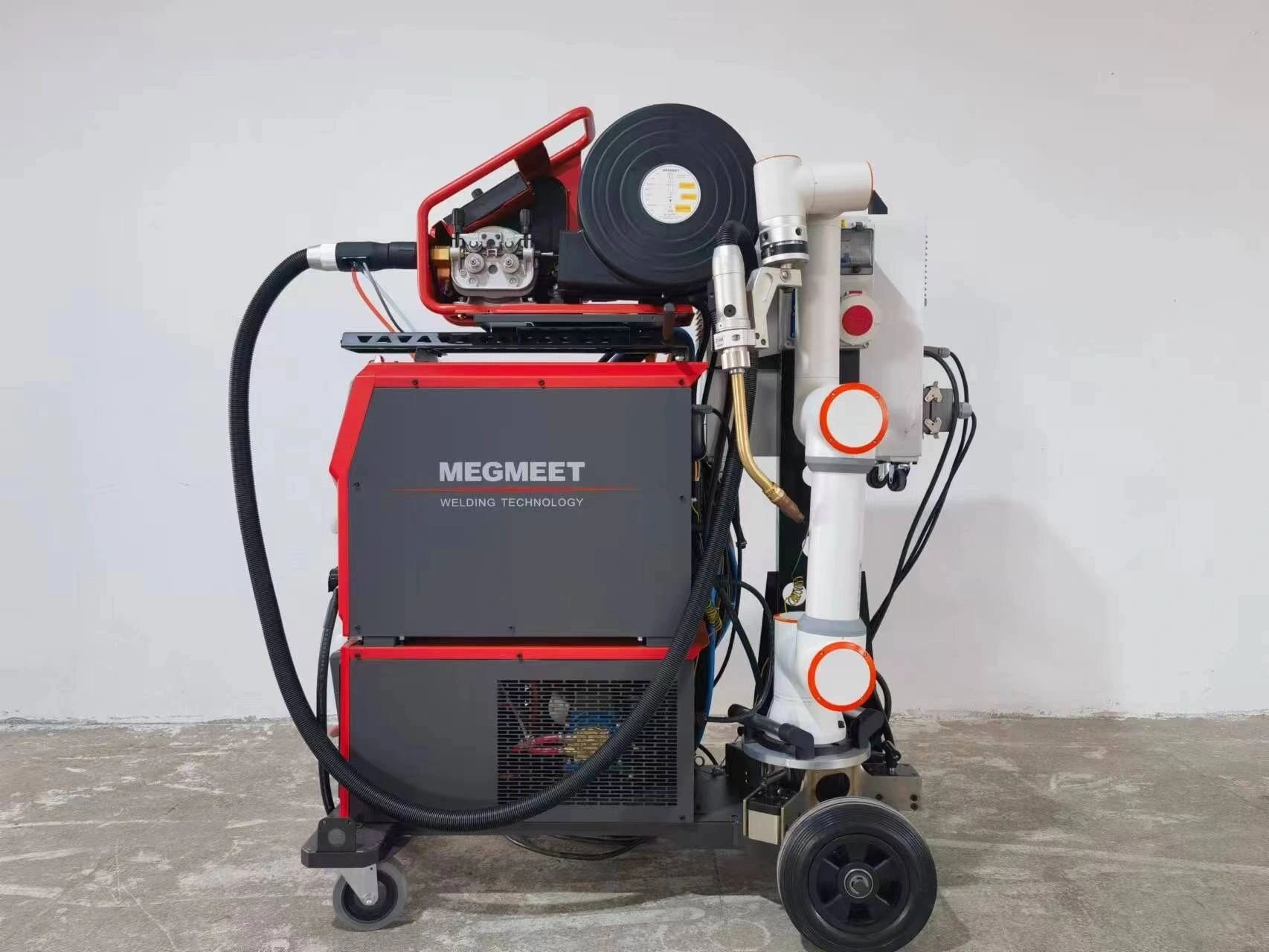

Cobots are now transforming fabrication shops through:
Consistent weld quality: Cobots maintain steady heat input and torch movement.
Hybrid collaboration: The human operator positions parts, while the robot performs precise weld passes.
Simplified setup: No complex programming; operators can manually guide the robot through the weld path.
Better safety: The robot handles arc exposure and fumes, keeping workers safe.
Because they’re smaller and more affordable than traditional robotic welding systems, cobots make automated welding accessible to small and medium manufacturers, not just large OEMs.
3. Machine Tending and CNC Automation
Machine tending—loading and unloading parts from CNC machines, lathes, or injection molding systems—is a perfect fit for collaborative robots. This task is repetitive and time-consuming for operators, yet ideal for robotic precision.

Cobots can:
Open and close machine doors
Load raw parts into the chuck or fixture
Remove finished parts and place them onto pallets
Wipe, blow, or inspect parts between cycles
By assigning these routine tasks to cobots, manufacturers can free human operators for supervision and quality control, significantly increasing machine uptime. Cobots can also run continuously, even during night shifts, creating a 24/7 “lights-out” production capability.
4. Material Handling, Sorting, and Packaging
Material handling is one of the broadest applications for collaborative robots. With various grippers, suction tools, or magnetic end-effectors, cobots can efficiently move, pack, and organize parts across a facility.

Common applications include:
Pick-and-place in electronics, food, or cosmetics production
Sorting products by shape, size, or barcode data
Packaging and labeling goods for shipment
Palletizing boxes at the end of production lines
Cobots are particularly valuable in logistics and e-commerce environments, where product types and volumes change frequently. Their mobility and quick redeployment make them ideal for agile operations—something traditional robots often struggle with.
5. Quality Inspection and Testing
Inspection and testing are critical for maintaining product reliability, especially in precision industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Collaborative robots equipped with cameras, sensors, and measurement tools can perform these tasks with consistent accuracy and repeatability.
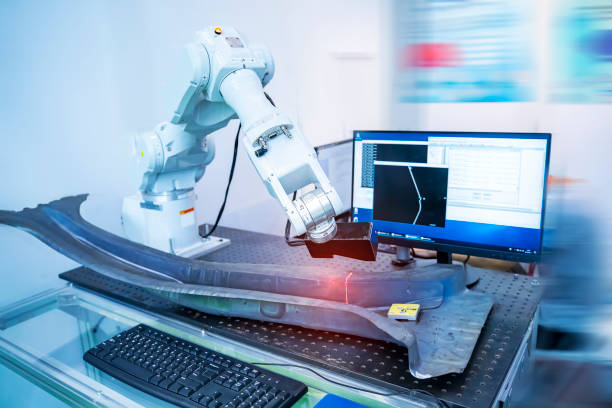

Examples include:
Checking part dimensions using 3D vision systems
Scanning for surface scratches, dents, or defects
Verifying alignment, assembly tightness, or solder quality
Running functional tests (e.g., pressing buttons or turning knobs)
Cobots reduce human fatigue and subjective error, ensuring consistent quality control around the clock. Plus, they can log inspection data directly into production software, enabling digital traceability and analytics-based process improvement.
6. Polishing, Sanding, and Surface Finishing
Surface finishing tasks—like polishing, grinding, or deburring—require constant force control and smooth, repetitive motion, which makes them perfect for cobot automation.
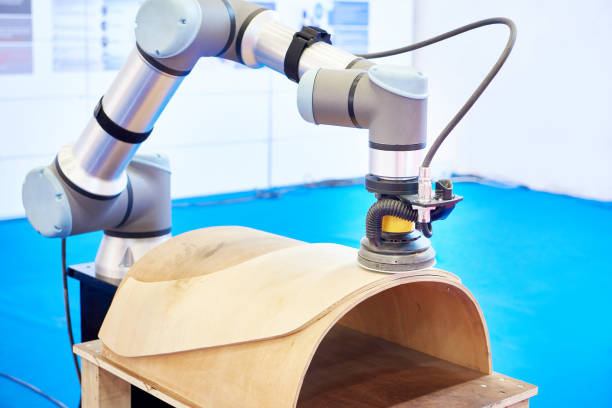
Collaborative robots equipped with force sensors can:
Deburr metal castings and machined parts
Polish stainless steel or aluminum surfaces
Sand composite materials evenly
Maintain a uniform finish on car bodies or appliances
Cobots excel at applying just the right amount of pressure—something even skilled human operators can find difficult to maintain consistently over time. This results in uniform texture, improved surface quality, and reduced rework.
Moreover, automating finishing operations protects workers from exposure to dust, vibration, and repetitive strain injuries, creating a safer work environment.
7. Painting, Coating, and Adhesive Application
Cobots are also gaining ground in painting and adhesive dispensing tasks, where precision and consistency are vital. With smooth motion control and programmable paths, they can apply coatings or adhesives evenly and efficiently.

Use cases include:
Spray painting small parts or enclosures
Applying adhesives, sealants, or lubricants
Dispensing uniform beads for sealing glass, panels, or trim
Coating metal and plastic parts with minimal overspray
Cobots not only enhance coating quality but also minimize material waste. Their ability to operate in enclosed or ventilated environments also improves worker safety by reducing exposure to fumes or chemicals.
8. Pick-and-Place in Electronics and Precision Manufacturing
The electronics industry relies on micrometer-level accuracy, making it a perfect playground for cobots. Their precision, repeatability, and gentle handling capabilities make them ideal for delicate component assembly.
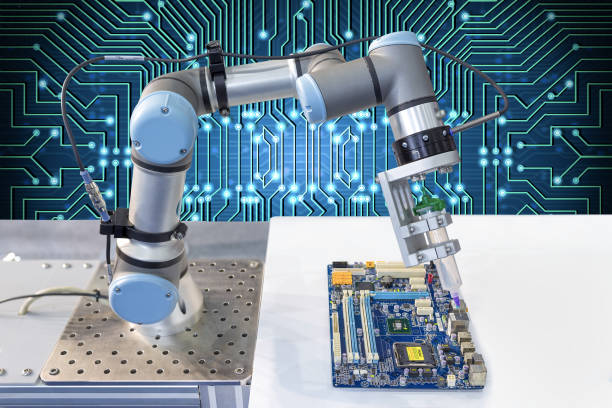
Cobots can:
Place chips or connectors on PCBs
Assemble smartphone and tablet components
Insert miniature parts into compact assemblies
Handle batteries and sensors in electric vehicle modules
Equipped with vision systems, cobots can detect and align small components even on fast-moving production lines. This makes them invaluable for manufacturers producing small, fragile, or high-value products that demand absolute consistency.
9. Palletizing and Depalletizing in Logistics
Cobots have become a game-changer for palletizing and depalletizing operations in warehouses, packaging plants, and distribution centers. They can stack boxes, bags, or cartons in pre-defined patterns, optimizing space and stability.

Key advantages include:
High-speed stacking of mixed-size items
Integrated vision for barcode and label detection
Easy reconfiguration for different product lines
Compact design for tight warehouse layouts
Collaborative palletizing systems are safer and more adaptable than traditional robotic cells. They’re especially useful for small-batch production or end-of-line automation in facilities where product dimensions frequently change.
10. Laboratory and Pharmaceutical Automation
Beyond manufacturing, collaborative robots are making a strong impact in pharmaceutical and laboratory environments. These sectors demand repeatable precision, sterile operation, and reduced human contact—all strengths of cobots.
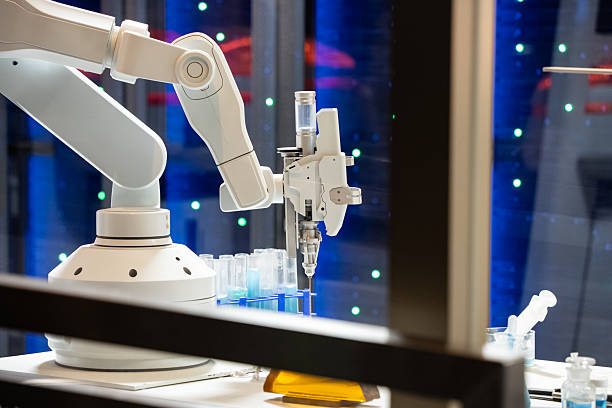

Typical applications include:
Automated sample preparation and pipetting
Vial filling, capping, and labeling
Transferring samples between analysis instruments
Sorting and storing laboratory containers
Cobots can operate in cleanroom environments and support 24-hour operation with consistent results. This not only increases throughput but also minimizes contamination risk—critical for pharmaceutical research and production.
Why Collaborative Robots Are Transforming Industry
The power of collaborative robots lies in their combination of flexibility, precision, and safety. They’re not massive, expensive industrial machines—they’re adaptable tools designed to work side by side with people.
Here’s why industries continue to adopt cobots at record speed:
Fast ROI: Many cobot installations pay for themselves in under a year.
Accessibility: No coding skills or complex safety setups required.
Scalability: Cobots can be reprogrammed and moved between lines easily.
Safety: Advanced sensors and torque controls ensure safe human interaction.
From welding and inspection to logistics and lab automation, cobots are driving the next generation of smart manufacturing—bridging the gap between human intuition and robotic precision.
Conclusion
Collaborative robots are no longer futuristic concepts—they’re everyday tools reshaping how factories operate. Their ability to blend flexibility with safety allows both large and small manufacturers to increase productivity, improve quality, and respond faster to market demands.
As we move further into 2025, cobots will continue to evolve—integrating better sensors, AI-based vision, and real-time data analytics. The factories that embrace them today will be the ones leading tomorrow’s automation revolution.
Related articles:
1. Cobot Welding Basics and Megmeet's Cobot Welding Solutions
2. Robots & Cobots Revolutionizing Welding Automation
3. How to Maximum your Productivity with Cobot Welding?
4. 5 Reasons to Use Cobots for Laser Welding: Power and Integration
5. Best 5 Arc Welding Robot Brands in the World (2024)














